Description
NR507 Week 7: CNS Sensory and Motor Disorders
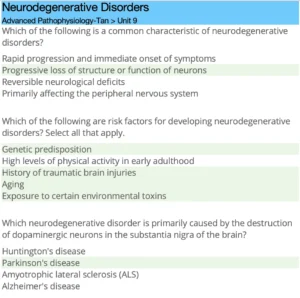


A nurse practitioner (NP) is caring for a client suspected to have Parkinson’s disease (PD). Based on the pathophysiology of PD, select the clinical manifestations the NP should anticipate. Select all that apply.
Muscle rigidity
Hyperreflexia
Bradykinesia
Tremor at rest
Postural instability
Increased dopamine levels
A 72-year-old client with a suspected diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is administered a test dose of levodopa. Which of the following indicates the effectiveness of levodopa in this client?
Increase in heart rate and blood pressure
Improvement in motor symptoms
Signs of allergic reactions
Improved cognitive function
A nurse practitioner (NP) is caring for a client with a newly diagnosed neurodegenerative condition. The client exhibits signs of cognitive decline, muscle weakness, and difficulty with coordination. Which of the following interventions would be most appropriate to include in the client’s plan of care?
Initiating a referral for physical and occupational therapy assessments
Advising the client to engage in complex mental exercises like solving puzzles
Prescribing anticoagulant medication to prevent ischemic stroke
Implementing a high-intensity exercise program to improve muscle strength
Which of the following statements best describes the pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis?
Myelin surrounding large nerve fibers is attacked by antibodies produced by the client’s immune system.
There is a progressive loss of dopamine-producing receptors in the substantia nigra.
Acetylcholine receptors are attacked by antibodies produced by the client’s immune system.
A viral infection attacks the client’s cranial nerves.
Place the following physiologic actions in the correct order in which they occur, from first to last.
- An action potential arrives at the axon terminal of a motor neuron.
- Synaptic vesicles release acetylcholine across the neuromuscular junction.
- Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle fiber’s membrane causing electrical depolarization.
- Muscle contraction occurs.
- Acetylcholine in the neuromuscular junction is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase.
- Muscle contraction stops………………………………..$20








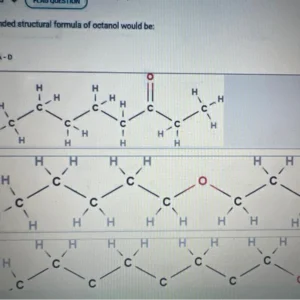

























Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.