Description
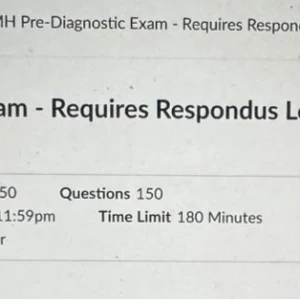
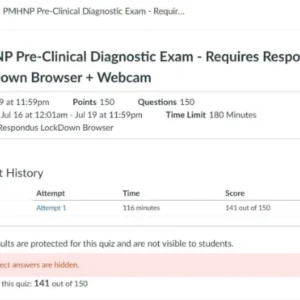
NR567 Week 4: Midterm Exam

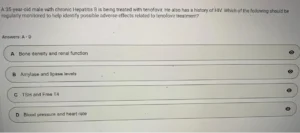

According to antimicrobial stewardship principles, which action should a provider avoid to prevent antibiotic resistance?
Answers: A – D
A Narrowing antibiotic therapy based on culture results
B Prescribing antibiotics for viral infections ✅
C Starting empiric therapy before cultures are obtained
D Prescribing the shortest effective duration of therapy
A 60-year-old patient hospitalized with symptoms of hospital-acquired pneumonia. Cultures reveal Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Which antibiotic combination is recommended?
Answers: A – D
A Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
B Piperacillin/tazobactam and tobramycin ✅
C Ceftriaxone and azithromycin
D Vancomycin and rifampin
A patient with Cushing syndrome is prescribed ketoconazole. Which of the following mechanisms does ketoconazole primarily utilize to manage the condition?
Answers: A – D
A It promotes adrenal insufficiency
B It blocks ACTH production from the pituitary gland
C It enhances the metabolism of cortisol
D It inhibits the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal glands ✅
A 72-year-old patient with a history of diabetes is diagnosed with cellulitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus that is methicillin-resistant. What is the best treatment option?
Answers: A – D
A Penicillin G
B Cefotaxime
C Vancomycin ✅
D Amoxicillin
A patient with a history of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is prescribed phenazopyridine for urinary discomfort associated with a UTI. What should the nurse consider when administering this medication to this patient?
Answers: A – D
A Phenazopyridine is safe for all patients, regardless of G6PD status
B The patient should avoid drinking fluids while taking this medication
C There is a risk of hemolytic anemia due to the patient’s G6PD deficiency ✅
D The medication will effectively treat the UTI
A 48-year-old male patient presents with symptoms of endocarditis. Cultures reveal Staphylococcus viridans. Which antibiotic combination is appropriate for initial treatment?
Answers: A – D
A Vancomycin and rifampin
B Penicillin G and gentamicin ✅
C Ceftriaxone and metronidazole
D Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
When considering influenza treatment in pregnant patients, which antiviral is preferred?
Answers: A – D
A Oseltamivir ✅
B Zanamivir
C Ganciclovir
D Valganciclovir
A patient with a confirmed diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis is prescribed amphotericin B. The nurse practitioner knows that treatment duration typically lasts how long for most systemic mycoses?
Answers: A – D
A 6–8 weeks ✅
B 1–2 weeks
C 3–4 weeks
D 12 weeks
A 70-year-old patient with a history of chronic liver disease is diagnosed with mild COVID-19 and is at high risk for severe disease. Which antiviral medication is contraindicated for this patient?
Answers: A – D
A Molnupiravir
B Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir ✅
C Remdesivir
D Oseltamivir
A patient in cardiogenic shock is most likely to benefit from which treatment approach?
Answers: A – D
A Vasoconstrictors for managing vasodilation
B Administration of IV fluids and blood products
C Use of inotropes and antiarrhythmics ✅
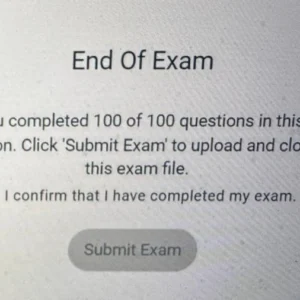
D Mechanical or surgical decompression………………………………………………purchase all the 100 questions and answers at $60 only
































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.