Description
NR507 Week 4: Urinary System Pathologies Common Diseases and Disorders
Which of the following are upper urinary tract infections (UTIs)? Select all that apply.
Cystitis
Pyelonephritis
Prostatitis
Urethritis
Ureter infection
Which of the following instructions should the nurse practitioner (NP) provide to a 20-year-old female being discharged with a urinary tract infection (UTI)? Select all that apply.
Wipe front to back
Empty the bladder every 5 hours
Drink at least 2 liters of water per day
Void after sex
Wear latex, rayon underwear
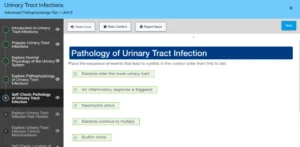
Place the sequence of events that lead to cystitis in the correct order from first to last.
- Bacteria enter the lower urinary tract
- An inflammatory response is triggered
- Neutrophils arrive
- Bacteria continue to multiply
- Biofilm forms
- Bacteria adhere to the bladder wall
- Client experiences pain with urination
Which of the following screening tests for benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) are indicated for complaints of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in the aging male? Select all that apply.
Digital rectal examination of the prostate
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level
Urinalysis
International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS)
Screening colonoscopy
Jamal Maduibike (pronouns he/him/his), 52 years old, is diagnosed with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). The client states, ”My brother was diagnosed with prostate cancer last year. Is this the same thing?” Which response by the nurse practitioner (NP) is most appropriate?
“BPH is an enlargement of the prostate gland that restricts the flow of urine but does not lead to cancer.”
“BPH is a malignant condition that will require chemotherapy and possibly surgery to remove the gland.”
“BPH is a benign tumor that does not spread to any other part of the body.”
“BPH can lead to prostate cancer, so you will be monitored closely over the next year.”
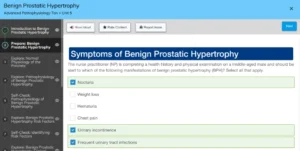
Moses Morgan (pronouns he/him/his), 72 years old, presents with complaints of urinary frequency and urgency that have become progressively worse over the last 6 months, waking to urinate more than five times at night and feeling like his bladder is never emptied. He admits to being embarrassed because he “leaks” after urination. When asked, Moses denies fever, weight loss, or bone pain. His medical history includes hypertension for which he takes prescribed atenolol 50 mg po daily and aspirin 81 mg po daily. His family history is negative for malignancy. A urinalysis was performed with negative results.
After completing a digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess the quality of the prostate, the nurse practitioner (NP) should be concerned with which finding(s)? Select all that apply.
A soft-smooth prostate
A lack of pain on palpation
A rubber-like quality of the prostate
A hard nodule
Blood on the glove after the examination………………………….$20
































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.